
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
After a long period of development, metal materials have penetrated into all aspects of life, especially in the field of industrial manufacturing, metal materials have very good mechanical strength, temperature resistance, aging resistance, dimensional stability are more excellent. But with the development of science and technology, various industries such as aerospace, automotive and other fields have increasingly high requirements for the use of materials to meet the premise of the use of performance, the application of materials also put forward new needs, such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, safety, etc..
With the development of the 3D printing industry, we can see that the application of 3D printing high-performance plastic scene is increasingly rich, more and more industries are through the 3D printing technology to solve the problems encountered in the manufacturing process, so through the 3D printing of high-performance plastic manufacturing in the end can replace the traditional process of manufacturing out of metal parts? In this issue, 3D printing technology reference will be from the material, process, design and performance of several aspects of the complete show.
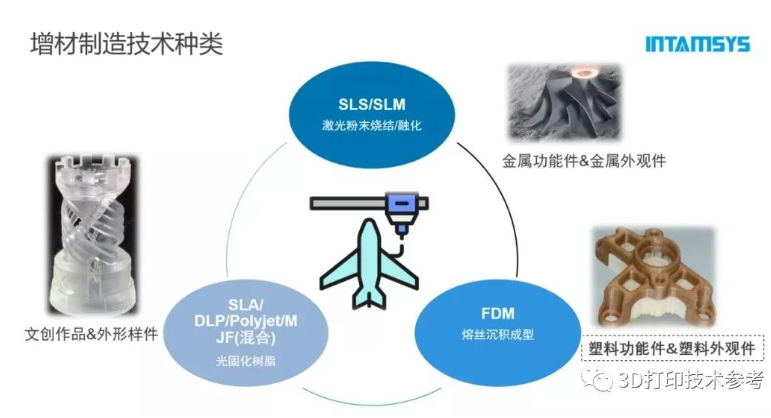
Types of additive manufacturing technologies
There are many types of additive manufacturing processes, among which FFF/FDM 3D printing technology is known for its own flexibility and versatility. The molding principle of this technology is not complicated, as the plastic wire is melted and extruded through a high-temperature nozzle, and the wire is stacked, cooled, and cured on the printing platform to obtain a solid layer by layer. Because the raw materials used are based on plastics that have been developed for more than 120 years, the parts printed by the FFF/FDM process have different material options and functional characteristics for various environments, such as superior mechanical properties, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, friction resistance, etc.

Classification of thermoplastic materials
01 Engineering plastics
Now the market mainly uses FFF/FDM 3D printing materials, there are engineering materials and high-performance special materials. Among the common engineering plastics, PC has very good wear resistance, temperature resistance and oil resistance; ABS is only about one-half of the cost of PC, and has good processability and very good plating performance, which can realize vacuum lamination or painting process, and the space for post-processing is relatively large. In addition, among the engineering plastics, there is also nylon, which has very good rigidity, strength, wear resistance and oil resistance, generally used in a large number of automotive interior and exterior trim and air conditioning ventilation ducts and other scenarios, but because the nylon material is easy to absorb water, so its dimensional stability is relatively weak, moisture absorption will become soft, toughness becomes large. In the face of high moisture scenarios, we can consider adding carbon fiber, such as nylon 12 carbon fiber, which has an equilibrium moisture absorption rate of only about 0.6%, and can maintain a very stable performance in daily use scenarios. In addition, the stiffness, strength and dimensional stability of nylon carbon fiber material are better, which is suitable for some scenes with high requirements for dimensional accuracy, such as positioning tooling.
02 High performance special materials
PPSU is resistant to hydrolysis, can withstand more than 100 steam sterilizations without damaging the mechanical properties, has excellent impact strength and is often used in medical devices with excellent results. ULTEM™ 1010 is preferred by many industries for its high strength, rigidity, wear resistance and dimensional stability at high temperatures, and is used in the electronics industry due to its excellent electrical properties, such as high temperature connectors and component holders. It is difficult to meet the requirements for light weight and flame resistance in the aerospace sector, ULTEM™ 9085 is suitable for making spare parts for aerospace components.
How 3D printing thermoplastics can replace metals through structural optimization
How can 3D printed thermoplastic parts be strength optimized for metal part replacement? There are several ways in which strength optimization can be achieved exactly.
01 Material side
-Find the ideal material based on a large library of materials
-Find the best performing materials from the market based on specified material properties
02 Process side
-Improve the denseness or fill type of the printed model
-Use larger nozzle sizes to achieve better interlayer strength
-Adjust the printing direction of the sample to avoid overloading in the Z-direction
-Increase shell thickness
03 Design side
-Avoid stress concentration
-Reduce the printing of fine structures, with secondary machining to achieve the final shape of the prototype
-Topology optimization based on finite element analysis
Performance differences between 3D printed plastic and metal parts
01 Flame resistance
Usually, if the car can reduce the weight of 10%, then the fuel savings can reach 6-8%, the weight reduction of materials is significant for energy saving and emission reduction, but most of the ordinary engineering plastics are flammable, which will increase the safety risks, plastics with flame retardant capabilities have very good application prospects, especially in the field of new energy vehicles today, the innate insulation of plastics is a major advantage.
02 Chemical resistance
Traditional manufacturing methods in order to meet the long-term use of metal materials in the friction conditions, usually using lubricants to reduce friction resistance, while increasing the risk of corrosion of materials. Plastics have inherent advantages in wear resistance, such as high-performance special plastics PEEK, with self-lubricating conditions and a relatively low coefficient of friction in the dry state, as well as good corrosion resistance, its chemical resistance is comparable to nickel steel, only dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid and some other strong corrosive solvents.
03 than strength
The most obvious difference between 3D printed plastic materials and metal is strength and heat resistance, as seen in the heat resistance curve, from ABS, which can withstand temperatures up to 80°C, to PEEK, which can withstand temperatures up to 260°C. Basically, they can meet the needs of everyday use in the environment. PEEK has some other better performance in the more demanding conditions of the space environment.
In addition, for the fatigue strength of material applications, the concept of specific strength can be introduced, which is the ratio of strength to density and can be interpreted as a comparison of the strength of two materials under the same mass. Like PEEK and PEI these two materials, their specific strength has been comparable to steel, so even in some of the more heavily loaded application scenarios, you can use plastic instead of metal.
04 Surface resistance
In conventional industrial production, the use of metal materials to produce tooling fixtures also has a very wide range of applications, but through the open-mold process to produce metal tooling time cycle is relatively long, the cost is also higher, which is also a more common need is anti-static. In this case, the use of Plastic 3D Printing to make tooling is also a very good choice. Some conventional engineering plastics, have a relatively high surface resistivity, which we know as insulating materials, so there is a risk of discharge in the production process. So can plastics also have some anti-static properties? The answer is yes. At present the mainstream way, is through the physical modification of plastic to achieve the effect of anti-static, such as the addition of carbon fiber, nanotubes, or even graphene in the raw materials, or choose some more moisture-absorbing materials, such as the aforementioned nylon material, it will improve the conductivity after moisture absorption, but will therefore sacrifice some precision.

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.